Research Assets & Grants
We invite researchers around the world to study FOXG1 syndrome, including the gene’s impact on brain development, and potential molecules that could improve symptoms.
We have developed and continue to develop a suite of assets such as mouse models and patient-derived iPSC lines that we make available for researchers to access.
Please see the assets available to researchers below.
FOXG1 Assets for Researchers
The FOXG1 Syndrome Patient Registry
Researchers interested in accessing FOXG1 de-identified patient information may request credentials by emailing registry@foxg1research.org and indicating the purpose of your research.
Our Advisory Board will review your request, and upon approval, you will be sent credentials to register and login at https://foxg1.beneufit.com
The FOXG1 Syndrome Digital Natural History Study, powered by Citizen Health.
To access the NHS data, contact registry@foxg1research.org and request Ciitizen NHS data.
Coriell FOXG1 Syndrome Stem Cell Biobank
includes:
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)
Lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs)
Fibroblast cell lines
DNA
To access the biobank samples click here
FOXG1 PostMortem Brain Tissue
Research using postmortem brain tissue can lead the way to a better understanding of the biological causes of FOXG1 syndrome, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and related neurodevelopmental conditions to identify targets for the development of new and effective treatments.
Thank you to the incredibly meaningful decisions made b parents in our community, there are FOXG1 brain samples available with the following two brain banks:
AutismBrainNet:
Qualified researchers from all over the world who are interested in studying FOXG1 syndrome as well as Autism Spectrum Disorder are eligible to apply to request postmortem brain tissue samples and related data from Autism BrainNet.
Information about tissue characteristics and availability can be found in the Autism BrainNet Tissue Catalogue at abn.sfari.org/catalogue.
All requests to use brain tissue samples and related data must be submitted through SFARI Base at sfari.org/resource/sfari-base.
For more information about the tissue application process, visit autismbrainnet.org/tissue-application or email requests@autismbrainnet.org.
Harvard Brain Bank:
Investigators will submit a request through the NIH NeuroBioBank portal with the case of IDs of the de-identified available FOXG1 brains. To access those case IDS, please email us for those IDs at research@foxg1research.org
FOXG1 Scientific Research Project Grants
The FOXG1 Research Foundation is providing grants to scientists to deepen the understanding of the biology of FOXG1 with the goal of identifying innovative therapeutic strategies and finding a cure.
For the next few years, these are the strategic focus areas:
Experiments designed to understand when, where, and levels of FOXG1 needed for normal brain development in mice
Experiments designed to understand the biophysical properties of FOXG1 mutations
Experiments designed to gain insights into the molecular and cell biological pathways regulated by FOXG1
If you're interested in pursuing a research grant, download a grant application below.
Note: As a non-profit patient organization, we do not pay university overhead fees as part of our grants.
FOXG1 Information for Researchers
FOXG1 EXPRESSION
Outside of the central nervous system, the expression of FOXG1 is very limited. It is expressed in the nasal retina, the anterior foregut, the anterior pituitary, and the otic vesicle (gives rise to the ear).
In the developing and adult brain:
· Cerebral cortex
· Hippocampus
· Striatum
· Basal ganglia
· Olfactory bulb
Image: Brain Atlas
Kawaguchi et al. Dev Bio 2016
Top: sections of mouse embryos at E11.5. The site of FOXG1 expression is coloured in blue.
Bottom: sections of mouse brain at early postnatal (A) and adult (B) stages showing FOXG1 sites of expression in blue.
Abbreviations: Tel: telencephalon, oe: olfactory epithelium, ov, otic vesicle, rp: raphke’s puch, fg: foregut, pit: pituitary
Tigani et al. Cereb. Cortex 2020
Left: section of the developing cortex (at embryonic day 16.5) in mice, showing expression of FOXG1 in red (bright) in the cortical plate. Right: higher magnification of the boxed region (a’). FOXG1 is expressed at low levels in neural progenitor cells lining the ventricle (asterisk) and at higher levels in the cortical plate.
In cells in the brain:
· Neural progenitor cells (NPCs)
· Neurons
· Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs)
· Astrocytes
Data from www.BrainRNASeq.org
FOXG1 FUNCTION:
· Neural stem cell self-renewal
· Proliferation versus differentiation switch
· Establishment of forebrain cell-type identity
· Excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) neuronal balance
· Cortical laminar organization
· Neuronal survival
· Mitochondrial bioenergetics
Phenotypes detected in Foxg1+/- mice
· Smaller forebrains than wildtype, mainly due to reduced cortical and hippocampal size
· Abnormal cortical laminar organization
· Corpus callosum agenesis
· Delayed myelination
· Poor performance in memory tasks
· Aggression
· Hyperactivity
· Reduced sociability and social novelty seeking
· Abnormal EEG (but not spontaneous seizures)
Phenotypes detected in postmortem brains (p.Glu154Glyfs*301 and p.Glu154*)
· Abnormal cortical laminar organization
· Absent myelination (possibly delayed)
· Almost absent OLIG2+ cells
· Reduced cortical cell numbers, particularly deep layer neurons and GABAergic neurons of the forebrain
· Corpus callosum agenesis
· Gliosis (increased GFAP-positivity)
· Calcified neurons
Unlocking the mysteries of common neurodevelopmental disorders via FOXG1
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS: PROPORTION MONOGENIC – 15-34%
FOXG1 variant identified in an individual with ASD and his similarly affected mother
FOXG1 gene dose associated with ASD diagnosis
SCHIZOPHRENIA: PROPORTION MONOGENIC HERITABILITY 70-80%
A schizophrenia-associated loci was shown to physically interact with and regulate FOXG1 expression
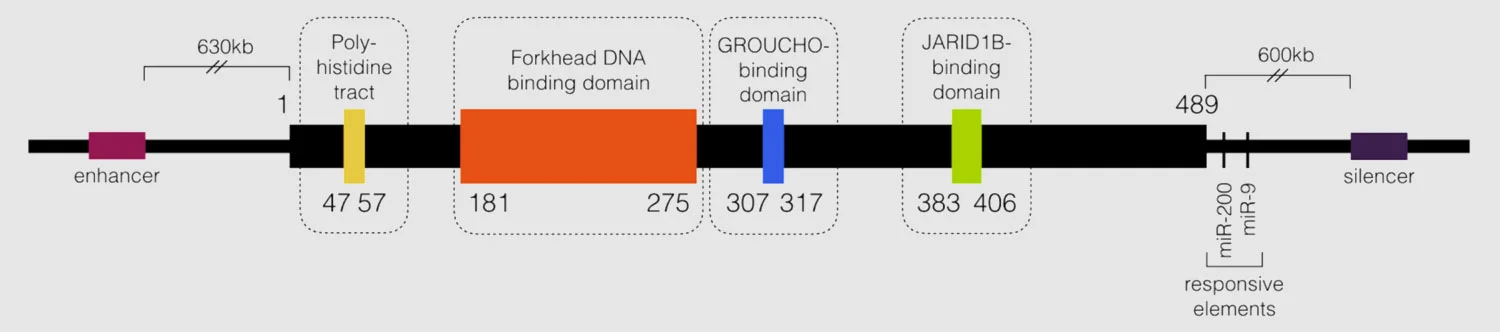
Expression of schizophrenia-associated gene, GRID1, found to be significantly elevated in FOXG1 patient-derived iPSC neurons and Foxg1+/- fetal mouse brainFunctional/regulatory elements in FOXG1
EPILEPSY :PROPORTION MONOGENIC – >40% in EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHIES
~87% of individuals with a FOXG1 mutation are diagnosed with epilepsy
Age of onset, seizure type, response to medication variable
All pathogenic missense mutations thought to occur in the forkhead DNA binding domain
Deletions including cis-acting regulatory elements but not coding region result in a FOXG1 syndrome phenotype